Architecture of Centralized Database System. Download Scientific Diagram
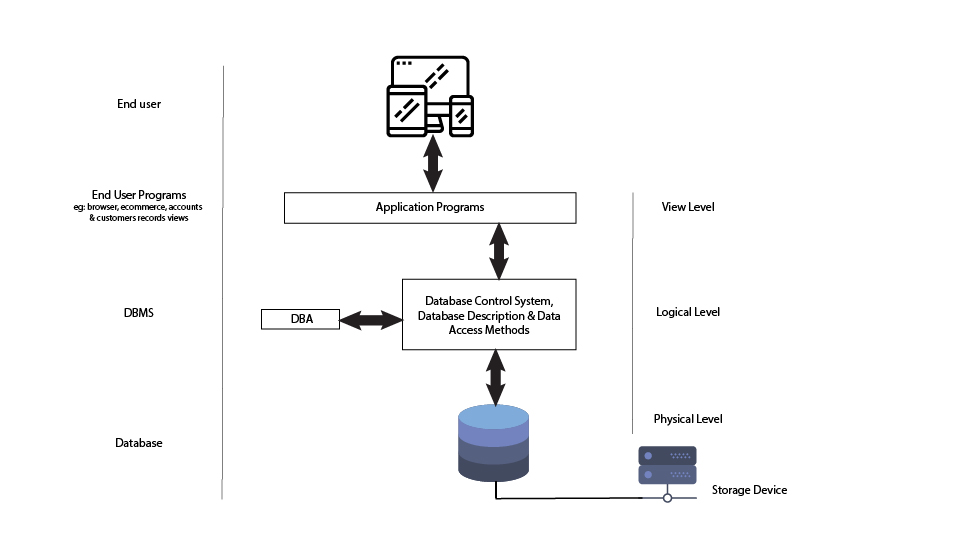
The structure of a Database Management System (DBMS) can be divided into three main components: the Internal Level, the Conceptual Level, and the External Level. Internal Level: This level represents the physical storage of data in the database. It is responsible for storing and retrieving data from the storage devices, such as hard drives or.
Database Management System Introduction Set 2 (3Tier Architecture)
Database tool that is tailored to suit specific needs of SQL developers. Works with SQL and noSQL DB in a smart way. Try free now

Database architecture design Download Scientific Diagram
Databases architecture design. This article provides an overview of the Azure database solutions described in Azure Architecture Center. Azure Database solutions include both traditional relational database management system (RDBMS) and big data solutions. RDBMS workloads include online transaction processing (OLTP) and online analytical.

DBMS Data Base Management System Edusera
Highlights: 1- Simplest DBMS architecture.. 2- All the components of DBMS, i.e., the server, database, and client, reside on a single system.. 3- The user can directly access the database.. 4- Used when data isn't changing frequently.. 5- Suitable for programmers, database designers, and single-user access.. 2. Two Tier Architecture. The 2-Tier architecture is the same as the basic client-server.

Unit 1 Lecture 3 Database System Architecture YouTube
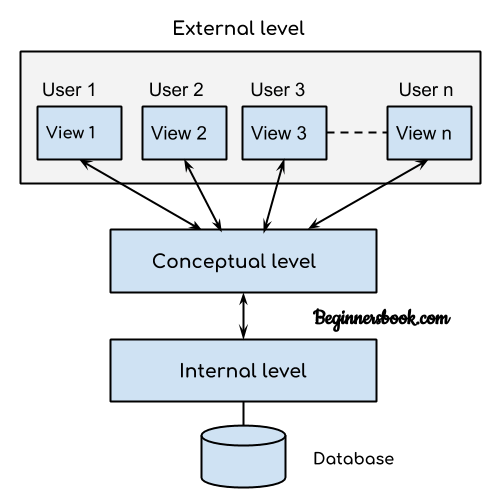
The simplest database system architecture is 1 tier where the Client, Server, and Database all reside on the same machine. A two-tier architecture is a database architecture in DBMS where presentation layer runs on a client and data is stored on a server. Three-tier client-server architecture consists of the Presentation layer (PC, Tablet.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dbdiagram.io---diagram-only-5c6c2b4746e0fb0001b35e35.png)
What Is a Database Schema?
A well-designed database architecture not only ensures data integrity and security but also plays a crucial role in optimizing performance and scalability. In this chapter, we will explore the fundamental concepts of database architecture, covering key components, models, and approaches that form the building blocks of a reliable database system.
The Complete Guide to Database Schema Edraw
For the main content, we start with a default template from the icon set, but this method can work with any existing diagram that benefits from layers. Onto a blank Draw.io canvas, drag the Physical Example 6 file. Ensure that the layer widget is enabled: The result is a drawing with a single layer:

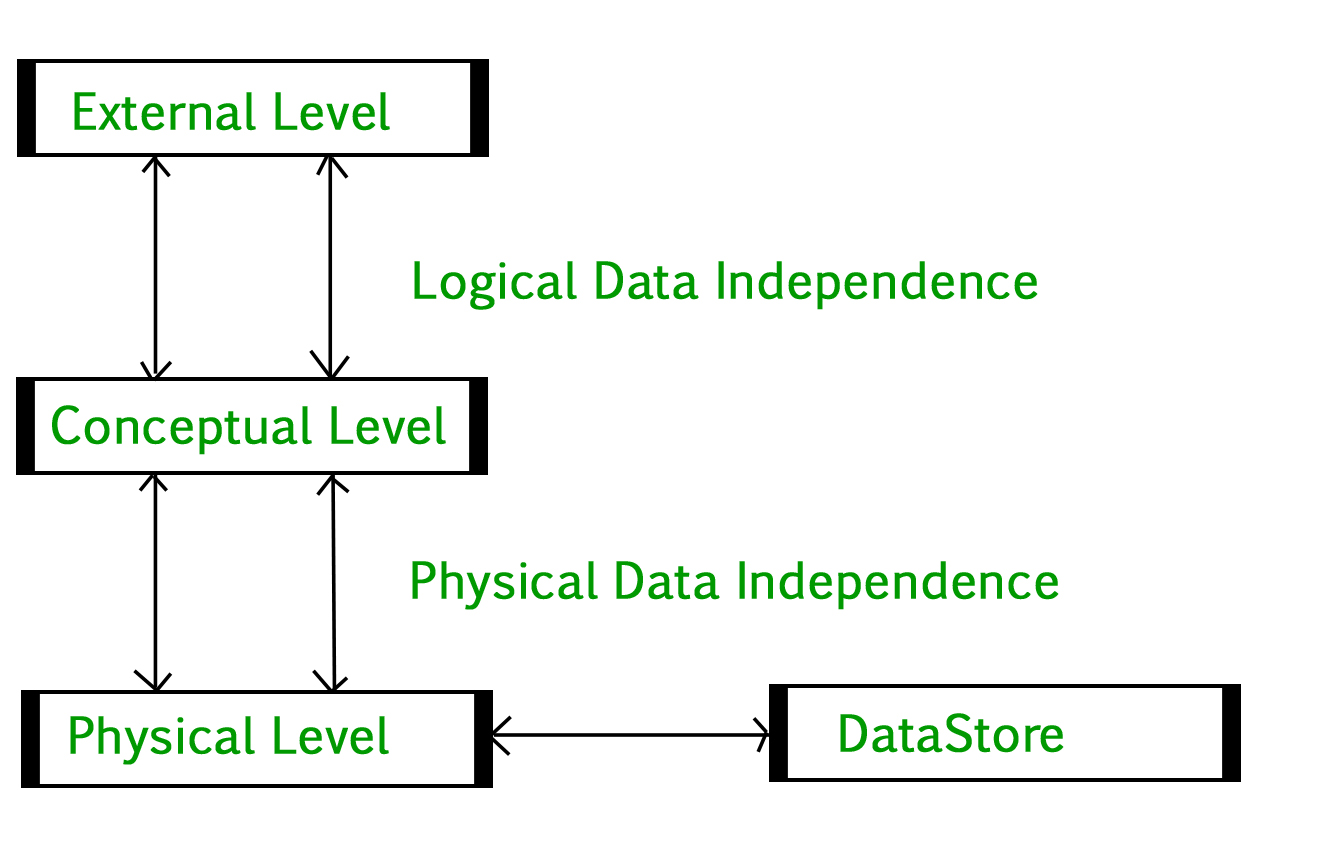
Overall Structure of DBMS
The above block diagram broadly explains about the interaction, the database architecture has three levels and they are as follows: External level. Conceptual level. Internal level. The inter connection of the above levels i.e. architecture of the database in DBMS is as shown in the below block diagram: Fig 2: Architecture of Database.

System Architecture Diagram
operators exist to request data from the database. These operators make calls to fetch data from the DBMS' Trans-actional Storage Manager (Figure 1.1, bottom), which man-ages all data access (read) and manipulation (create, update, delete) calls. The storage system includes algorithms and data structures for organizing and accessing data on disk

Database Architecture Diagram
Types of DBMS Architecture. Database architecture can be seen as a single tier or multi-tier. But logically, database architecture is of two types like: 2-tier architecture and 3-tier architecture. 1-Tier Architecture. In this architecture, the database is directly available to the user. It means the user can directly sit on the DBMS and uses it.
What Is Database Architecture Explain With Diagram Design Talk
The database design process. A well-structured database: Saves disk space by eliminating redundant data. Maintains data accuracy and integrity. Provides access to the data in useful ways. Designing an efficient, useful database is a matter of following the proper process, including these phases: Requirements analysis, or identifying the purpose.
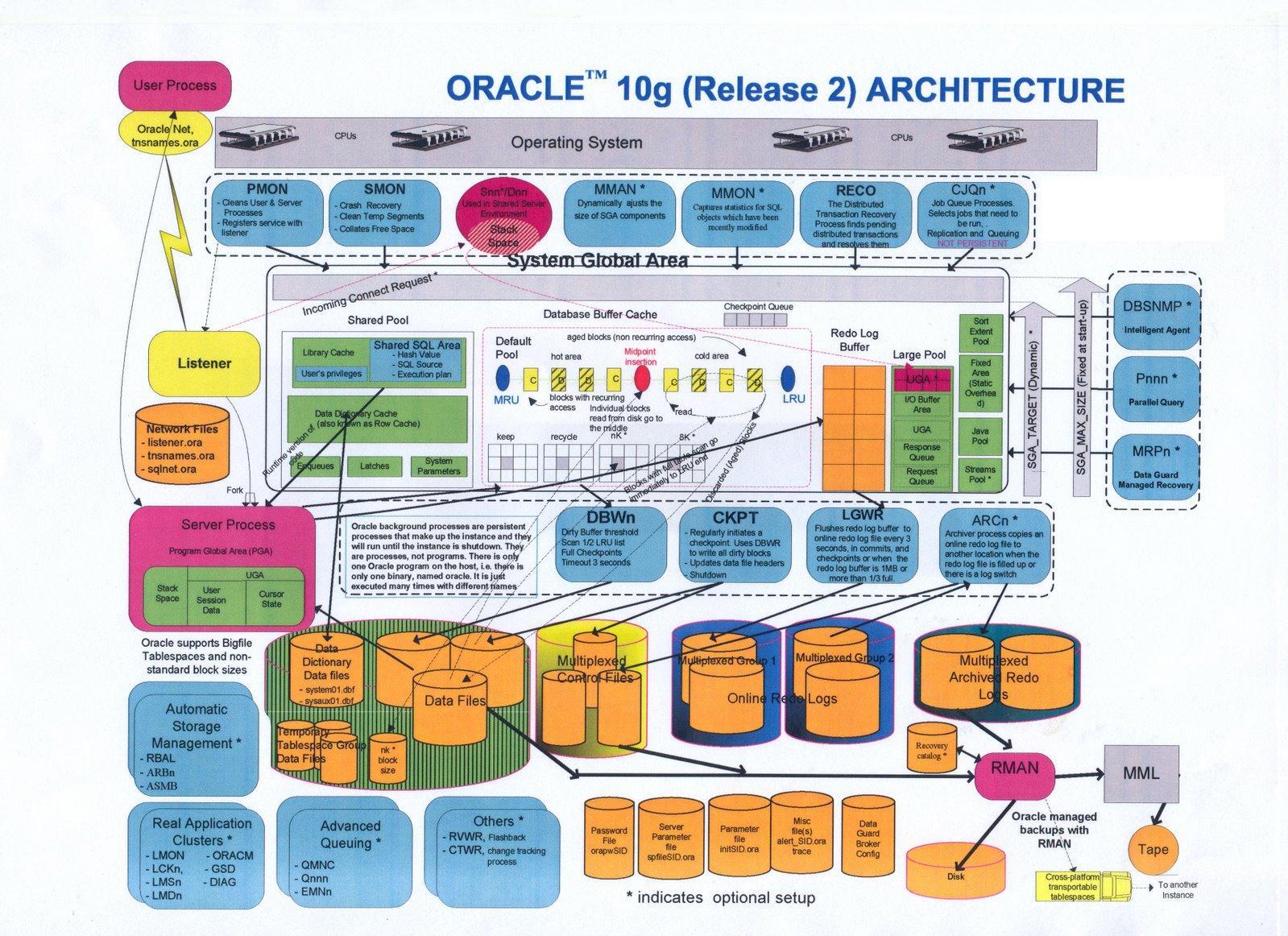
Oracle 数据库体系结构图高清无码大图分享 Oracle Life 云和恩墨,成就所托!
Oracle Database 18c Technical Architecture. Slide 1 of 29. Database Server. An Oracle Database consists of at least one database instance and one database. The database instance handles memory and processes. The database consists of physical files called data files, and can be a non-container database or a multitenant container database.
Database management system (DBMS) and Its architecture. Zerosack
Suppression of details of data organization and storage. Highlighting of the essential features for an improved understanding of data. Includes basic operations. Retrievals and updates on the database. Dynamic aspect or behavior of a database application. Allows the database designer to specify a set of valid operations allowed on database objects.
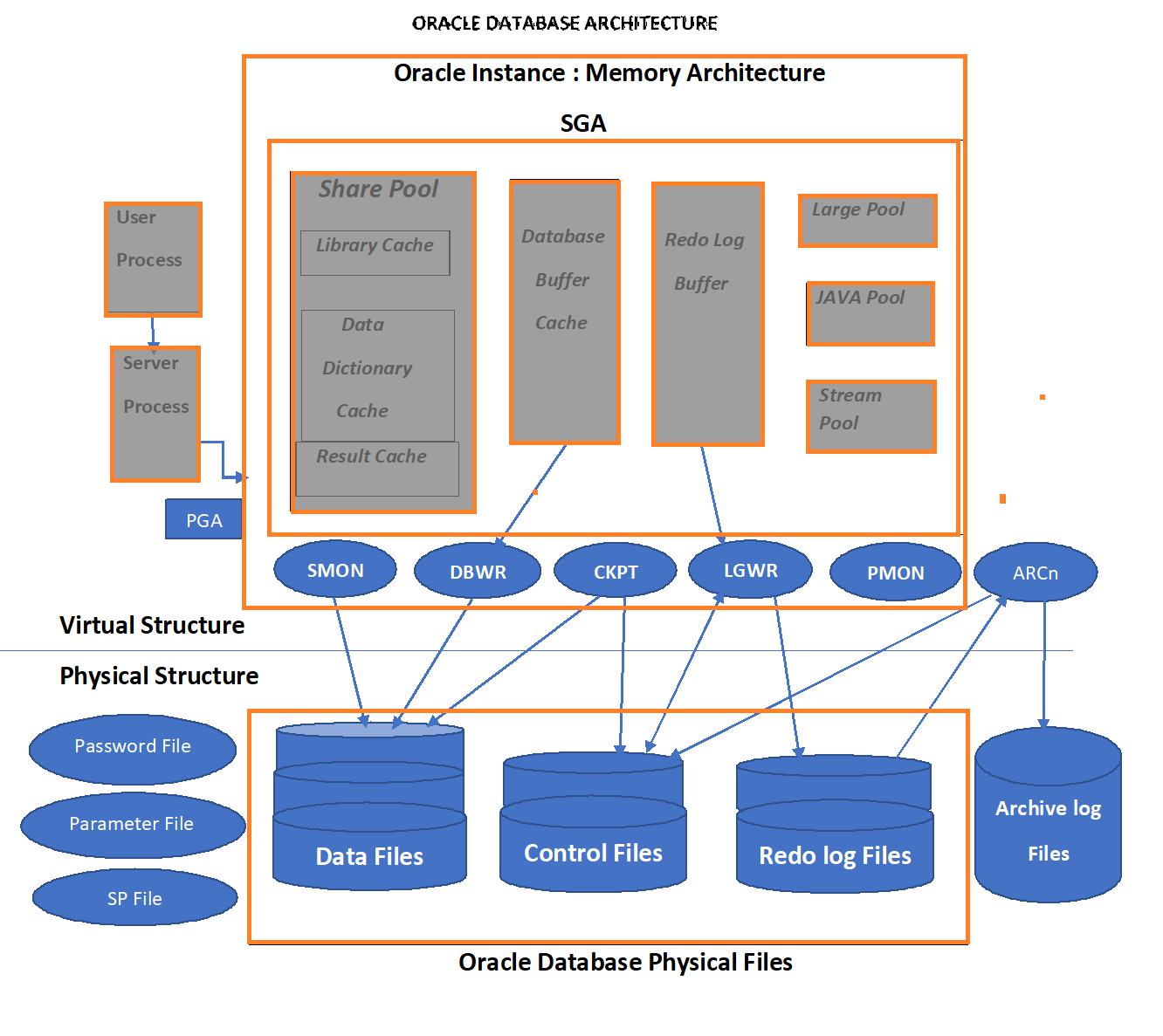
Oracle DBA concepts, DBA tutorials for Beginners , Oracle helps Oracle database Architecture
Data architecture diagram. As the name suggests, data architecture diagrams demonstrate how and where the data flows, is processed, and used. It includes components that define how data is collected in the system. If you are looking for ways to update and streamline data storage resources you would turn to a data architecture diagram.
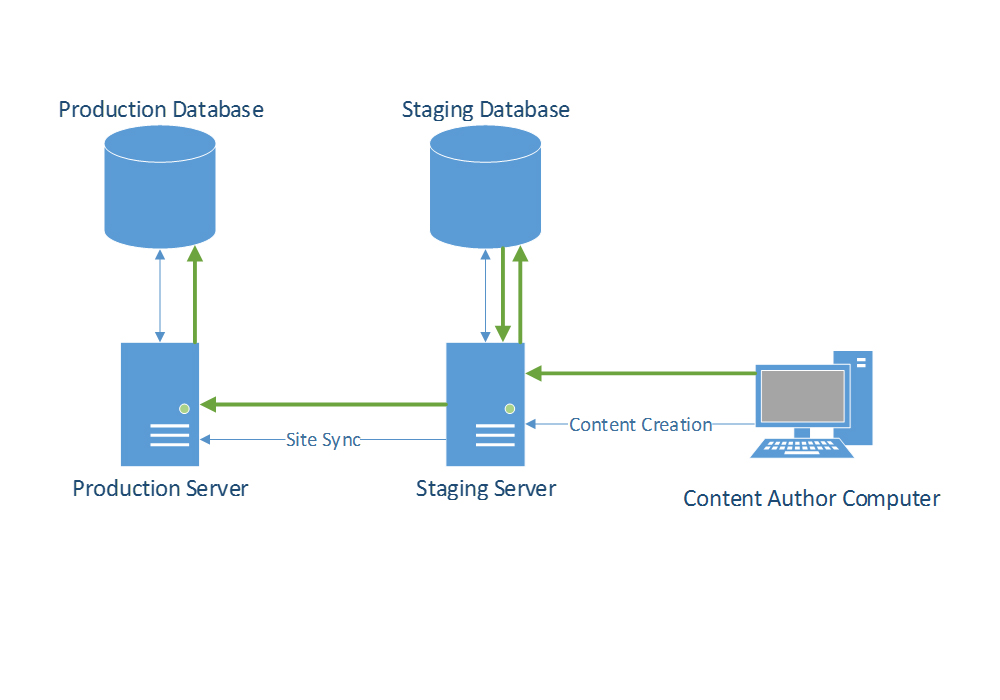
[DIAGRAM] Software Development Infrastructure Diagram
Database architecture describes how a database management system (DBMS) will be integrated with your application. When designing a database architecture, you must make decisions that will change how your applications are created. First, decide on the type of database you would like to use. The database could be centralized or decentralized.
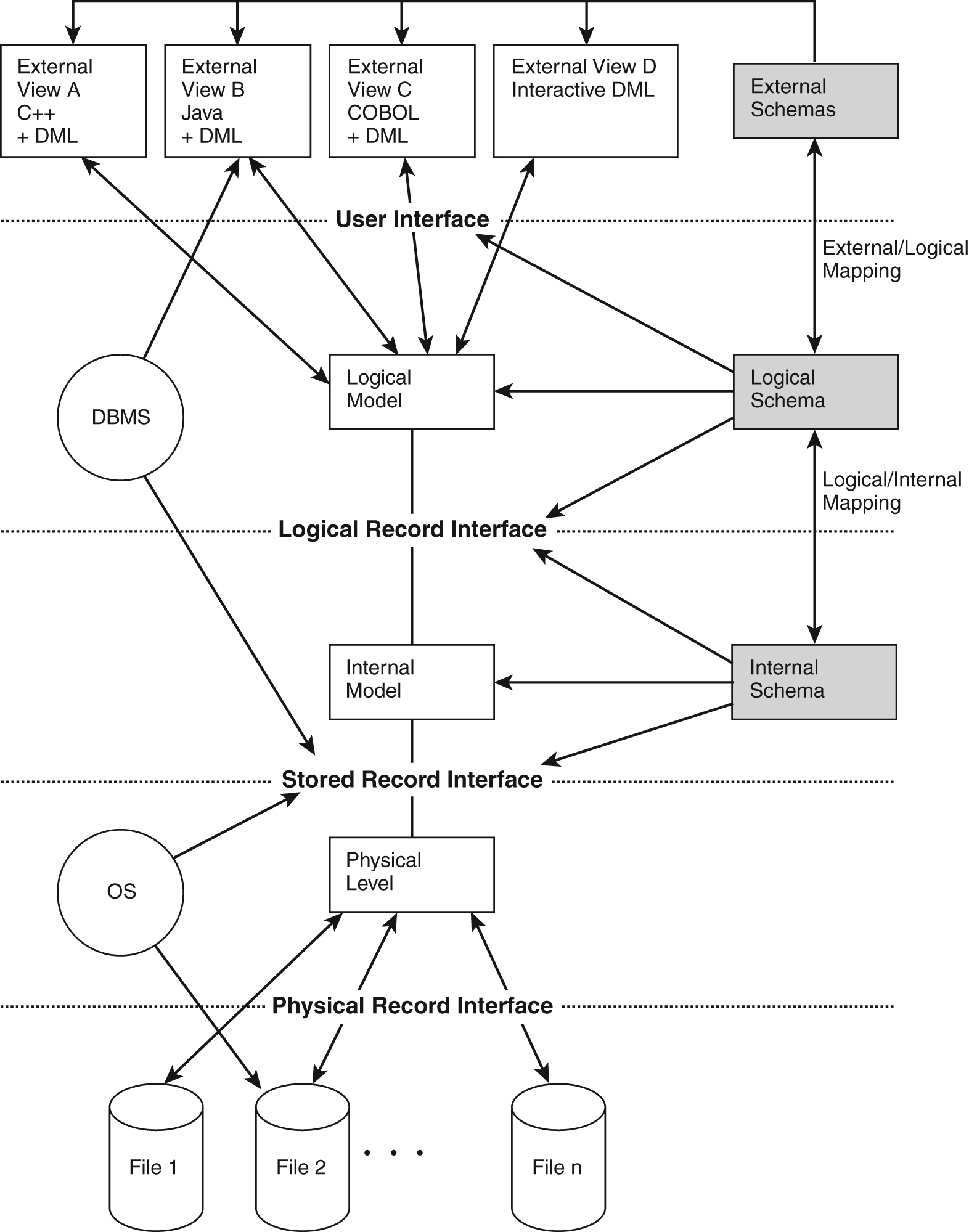
Conceptual Er Diagram
1.2. Architectural Fundamentals #. Before we proceed, you should understand the basic PostgreSQL system architecture. Understanding how the parts of PostgreSQL interact will make this chapter somewhat clearer. In database jargon, PostgreSQL uses a client/server model. A PostgreSQL session consists of the following cooperating processes.